Definition of Icterus and Jaundice
Definition of Icterus:
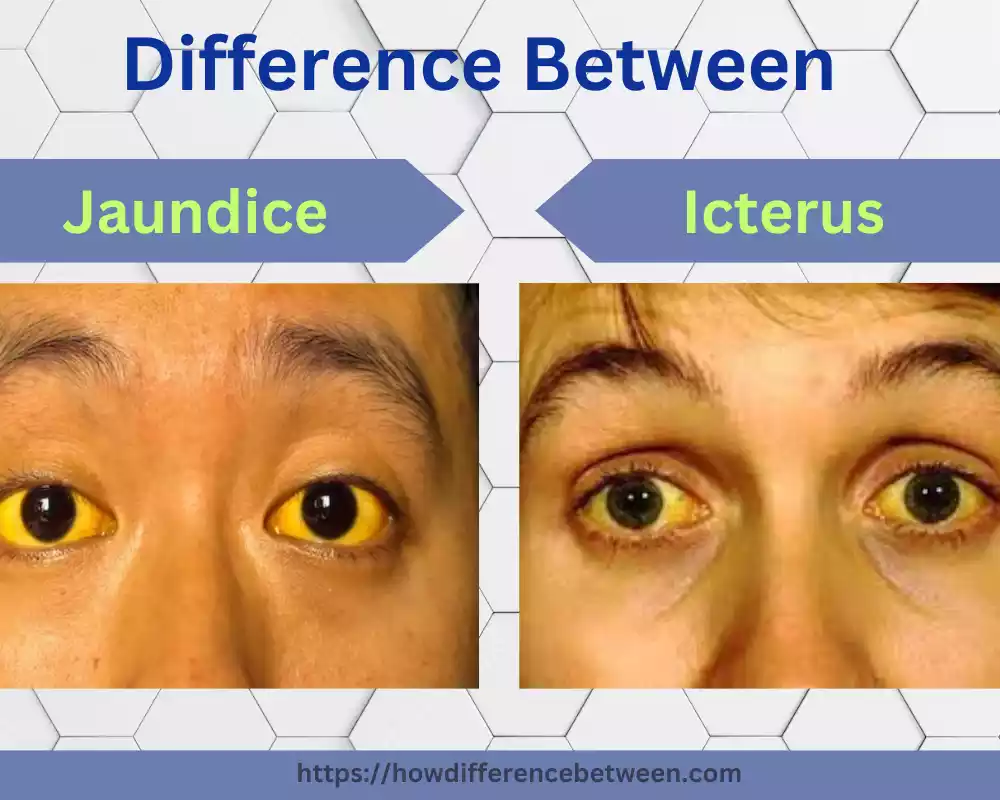
Icterus refers to any yellow discoloration on skin, mucous surfaces or whites of eyes caused by accumulations of bilirubin; an amber colored pigment created when red blood cells break down in your tissues and accumulate over time. Jaundice is another name for it.
Symptoms often accompany medical issues that impact liver, gallbladder or bile canal health as a whole; Icterus results from its accumulation, often related to liver disorders like gallbladder conditions affecting liver gallbladder health issues while its cause comes from accumulations of this amber-h-colored pigment found when red blood cells breakdown.
Definition of Jaundice:
Jaundice, commonly known by its yellowing of skin, mucous membranes, and eyes is caused by elevated levels of bilirubin produced as the by-product of hemoglobin breakdown within red blood cells and processed and excreted normally by liver; when liver’s ability to properly process or excrete this by-product fails due to liver illness or obstruction in bile canals this build-up of bilirubin accumulates, leading to jaundice symptoms – but many other conditions could also cause jaundice symptoms as underlying liver disorders play a part.
Importance of distinguishing between the two conditions
Importance of Differentiating Icterus from Jaundice:
- Accuracy in Diagnosis: Correct identification and treatment are dependent upon being able to differentiate between icterus and jaundice, with healthcare professionals understanding both causes and possible treatments more efficiently by knowing exactly which condition exists. This allows healthcare workers to select an effective path forward.
- Differentiate Causes: Both Icterus and Jaundice may have various causes. Icterus typically results from excessive red blood cell breakdown or specific medications; jaundice could stem from liver diseases, hepatitis, gallstones or bile duct obstruction – it’s important to identify all potential factors so treatments and management plans can be targeted accordingly.
- Treatment Approach: Understanding the differences between icterus and jaundice is vital when choosing appropriate approaches to their respective treatments, which vary based on underlying cause; treating liver disorders that cause jaundice could require specific medication or interventions tailored specifically for that condition, while managing side-effects from medication might mean either increasing dosage or switching treatments altogether.
- Prognosis and Monitoring: Making the distinction between icterus and jaundice helps doctors assess prognosis and follow progression of conditions like these more easily, since each has a distinctive course and potential complications that must be monitored closely by healthcare providers, along with managing strategies as needed to achieve best possible outcome for their individual patients. Accurate diagnosis allows appropriate monitoring, including responding quickly to treatment regimens while adapting management plans as necessary.
- Communication and Patient Education: Differentiation between Icterus and Jaundice is integral for effective healthcare communication between healthcare professionals and their patients, as it allows accurate explanations of each condition’s causes, treatment options and potential outcomes. Informing patients of their specific diagnosis helps them better comprehend it while being an active part of their own care team.
So it is of vital importance that healthcare providers can differentiate between icterus and jaundice for accurate diagnosis, targeted treatments, monitoring, effective communication with their patients, as well as optimal patient outcomes.
Icterus
Icterus (also referred to as jaundice) is a medical condition characterized by yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membranes, and whites of the eyes. This occurs due to an accumulation of bilirubin produced during red blood cell breakdown accumulating in body tissues, producing yellow pigmentation of discolored areas on these organs and surfaces.

Icterus can be caused by various causes, including liver dysfunction, gallbladder issues or obstruction in bile ducts. When your liver cannot process bilirubin effectively or due to obstructions preventing its flow into the bloodstream it builds up and eventually shows itself as yellow in your bloodstream, eventually manifesting as Icterus symptoms.
Symptoms of Icterus can range from yellowing of skin, eyes and mucous membranes; dark urine; pale stools; fatigue; loss of appetite and abdominal pain to name just some of its characteristics. Their severity will depend on both its root cause as well as any accumulation of bilirubin.
Healthcare professionals may conduct various diagnostic tests in order to diagnose icterus. This may involve conducting blood tests that measure bilirubin levels, liver function tests, imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan and, sometimes, liver biopsy; all designed to determine its source and assist with appropriate treatments.
Treatment for Icterus will depend on its source. Treatment might involve managing liver diseases, extracting gallstones or clearing away obstructions to the bile ducts as necessary; while supportive measures such as adequate hydration, rest and diet could also aid recovery from Icterus.
Individuals experiencing symptoms of icterus must seek medical advice as soon as they begin experiencing them, to ensure timely diagnosis and effective treatments to address its root causes, ease symptoms and avoid potential complications associated with it. Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in diagnosing and managing this condition for maximum patient comfort and outcomes.
Jaundice
Jaundice, or jaundice-like conditions, are medical disorders characterized by yellowed skin, eyes and mucous membranes caused by increased levels of bilirubin– a yellow pigment produced from red blood cell breakdown– in your bloodstream.
Jaundice can have several potential causes, most often stemming from liver malfunction. Diseases such as hepatitis, cirrhosis and infections that impair liver functioning often impair its ability to effectively process bilirubin thus leading to its buildup in the body and cause jaundice symptoms. Other contributing factors may include gallstones blocking bile ducts; certain medications; blood disorders or hereditary conditions which alter its metabolism causing accumulation.
Jaundice can be identified by yellow discoloration of skin, eyes and urine. Alongside yellowing symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal pain, dark urine production and pale stool production as well as symptoms like dark urine discharged after passing stool darkened with yellowish hue, itching or nausea may arise as additional manifestations.
Diagnosing jaundice involves a comprehensive process encompassing clinical evaluation, physical exam and various diagnostic tests. Blood tests typically used to measure bilirubin levels and liver function tests are often employed, along with ultrasound or CT scans used for imaging evaluation purposes as well. Imaging may be utilized for evaluation of liver structures as well as bile ducts; in certain instances liver biopsies might even be necessary for an in-depth evaluation.
Treatment for jaundice depends on its cause. Addressing each specific cause causing jaundice is key, including antiviral medications for hepatitis, lifestyle modifications to address liver disease or surgery to remove gallstones; supportive care such as rest, hydration and diet is equally vital in aiding recovery.
Individuals Experiencing symptoms of jaundice should seek medical advice Immediately. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatments can address its underlying cause while alleviating symptoms and preventing complications related to jaundice. Healthcare providers play a vital role in diagnosing and managing jaundice for maximum efficacy for patient results.
Differences between Icterus and Jaundice
Differences Between Icterus and Jaundice:
1. Underlying Causes:
- Icterus: This condition can be brought on by factors like an increase in red blood cell breakdown or taking certain medicines that disrupt cell adhesion and formation, among others.
- Jaundice: Jaundice may be caused by liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis), gallstones, bile duct obstruction or any condition affecting bilirubin metabolism.
2. Mechanism of Development:
- Icterus: This condition occurs when there is an accumulation of bilirubin within body tissues due to impaired processing or elimination.
- Jaundice: Jaundice results from an increase in bloodstream bilirubin due to liver dysfunction or obstruction.
3. Display of Symptoms and Signs:
- Icterus: One of the primary symptoms of Icterus is yellow discoloration of skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Other potential indicators may include dark urine production, pale stool colors and fatigue as well as loss of appetite or abdominal discomfort.
- Jaundice: Jaundice manifests as yellowing of skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Other symptoms may include fatigue, itching abdominal pain dark urine and pale stool.
4. Diagnostic Tests for Icterus:
- Icterus: Icterus can usually be diagnosed through various means such as measuring bilirubin levels in blood samples, liver function tests, imaging studies (such as ultrasound or CT scanning) and biopsy of liver tissue.
- Jaundice: For diagnosing jaundice, similar diagnostic measures may be applied, including blood tests to measure bilirubin levels and liver function tests, imaging studies and, when necessary, liver biopsy procedures.
5. Treatment Approaches for Icterus:
- Icterus: Its Behandlung for icterus typically centers on treating its source. This could involve making adjustments to medications or red blood cell breakdown remedies as needed or discontinuing drug that cause symptoms associated with iterus.
- Jaundice: Treatment options vary according to its source, such as antiviral drugs for hepatitis, lifestyle modifications for liver disease or gallstone surgery as well as specific therapies directed towards treating jaundice directly.
Both terms for yellow discoloration, icterus and jaundice, may often be used interchangeably; their distinction lies in their causes, including their etiologies and mechanisms of development, which could impact diagnosis or treatments options.
Similarities between Icterus and Jaundice
Icterus resembles jaundice:
- Yellow Discoloration: Both icterus (characterized by yellowing of skin and eyes) and jaundice (characterized by yellow discoloration of mucous membranes and skin) can result in Yellowing due to an accumulation of Bilirubin within tissues, leading to Yellowing Discolorations.
- Liver Dysfunction: Liver Dysfunction can play an essential part in both conditions; both Icterus (Jaundice) and Icterus may result from it.
- Diagnostic tests used for both icterus and jaundice have similar procedures: Blood tests to measure bilirubin can be found among liver function tests while imaging techniques such as ultrasound or CT scans may help assess liver health; in more serious cases a liver biopsy may also be necessary for further examination.
- Jaundice and icterus may both be linked to increased red blood cell breakdown: Icterus-related red cell loss contributes to elevated levels of bilirubin accumulation while conditions like hemolytic anemia could trigger jaundice symptoms.
- Importance of Medical Attention: Both Icterus (characterized by yellow tint) and Jaundice are medical conditions which must be assessed and managed effectively to avoid potential complications. For this reason, early diagnosis, identification of causes, and application of appropriate therapies must all take place quickly in order to address them successfully.
Although similar, icterus and jaundice differ considerably by being yellow discolorations disorders with similar etiologies and possible causes; there can be distinct distinctions in diagnosis options available depending on underlying issues that could contribute.
Application of Icterus and Jaundice
Application of Icterus and Jaundice:
- Medical Diagnosis: Healthcare professionals employ the terms icterus and jaundice to refer to discolorations of skin, eyes and mucous membranes due to infection or injury, usually yellow in hue. They may use these terms during diagnostic examination of patients exhibiting symptoms like yellowing of skin tone and dark urine production as well as pale stool production; accurate identification and differentiation help establish cause as well as guide treatment decisions accordingly.
- Treatment Planning: Distinguishing between Icterus and Jaundice is essential in designing an effective treatment plan, since their respective causes determine which interventions to use; for instance, viral hepatitis may require antiviral medicines while, if the cause for an Icterus episode lies within medication side effects such as increased dosage or switching out for another drug altogether; treatments must therefore be tailored specifically to optimize results.
- Management of Liver Disorders: Icterus and jaundice frequently accompany liver dysfunction. Understanding their distinction is paramount when treating diseases like hepatitis, cirrhosis or infections of the liver; thus providing healthcare providers an opportunity to provide tailored care that monitors progression of liver disorders more closely.
- Patient Education: Communication and patient education play a central role in managing icterus and jaundice. Healthcare providers can explain its causes, treatment options and lifestyle modifications to both patients and caregivers alike, while teaching individuals about follow-up visits, taking medications regularly as prescribed and engaging in self-care practices will enable them to actively take charge of their health management.
- Research and Clinical Studies: Differencing Icterus From Jaundice is crucial in medical research and clinical studies, where researchers must quickly classify cases to study causes, risks factors, treatment outcomes, potential complications associated with these conditions and more accurately define them in order to advance medical advancement in this area. By differentiating between Icterus And Jaundice they are better equipped with accurate data for analysis which in turn advances advancements within this field.
Icterus and jaundice play an indispensable role in medical diagnosis, treatment planning, managing liver disorders, patient education and research. Accurate differentiation between them ensures appropriate care is delivered while optimizing treatment outcomes and expanding medical knowledge in hepatology.
Conclusion
Icterus and Jaundice are medical conditions that can cause yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. While icterus refers to increased bilirubin levels in the blood, jaundice is the visible symptom of this condition. Early detection and proper medical care are essential for managing these conditions effectively. By taking preventive measures and seeking timely treatment, individuals can lead healthier lives.