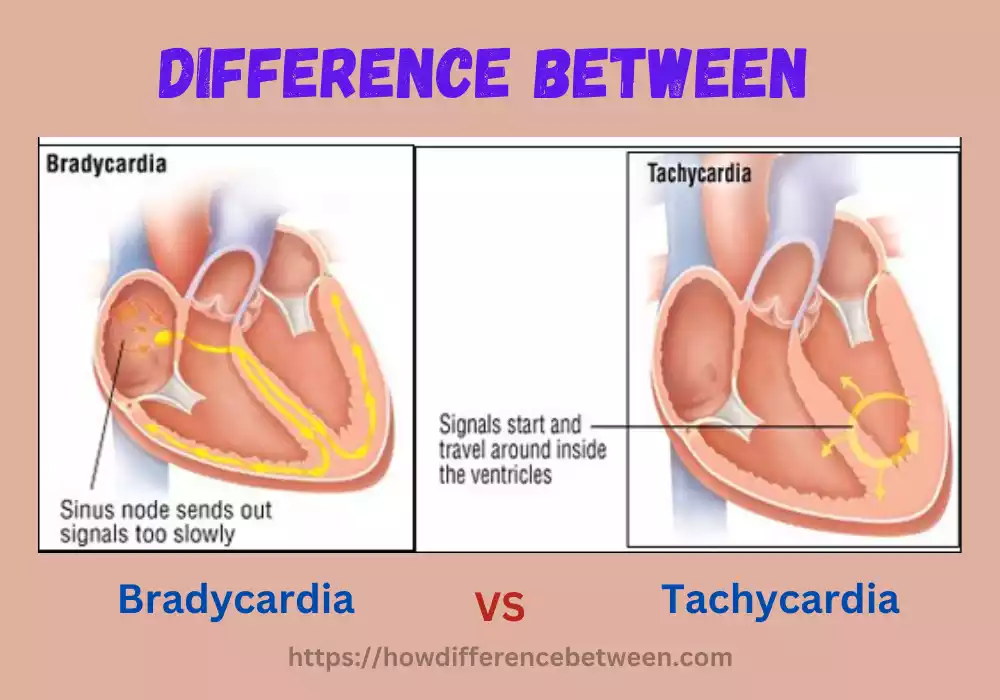
Tachycardia and Bradycardia are two conditions that affect the heart rate. While tachycardia refers to a heart rate that is too fast, bradycardia is characterized by a heart rate that is too slow. Both conditions can have various causes and symptoms, and it’s important to understand the differences between them. In this article, we will delve into the definitions, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for both tachycardia and bradycardia.
Definition of Tachycardia
Tachycardia, medically speaking, refers to an elevated heart rate exceeding what would typically be considered normal resting rates – typically 60 – 100 beats per minute in adults – typically anywhere from 100 BPM and higher, although the exact threshold may differ based on factors like age or health status.
Tachycardia may be caused by many different things, including physical stress or emotional strain, medication side effects and medical conditions; and the root causes of heart Disease. It’s essential to recognize that tachycardia itself does not pose a danger, rather it serves as an indicator of an underlying health problem affecting people of any Age, from infants to the Elderly.
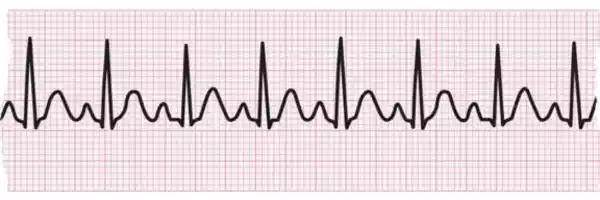
Untreated or improperly managed Tachycardia may lead to various health-related problems such as diminished circulation of blood to organs, increased risk of blood clot formation, heart failure, or cardiac arrest; hence timely diagnosis and proper management is vital in order to avoid problems while improving overall health and fitness.
Causes of Tachycardia
- Exercise and physical activity: As soon as you engage in strenuous activity or exercise, your heart naturally speeds up significantly to meet increased oxygen needs for your body. This natural physiological reaction is commonly known as exercise-induced or physiological tachycardia.
- Stress and anxiety that is emotional: Arousing strong emotions like stress, anxiety, fear, or excitement may trigger the production of hormones that cause stress such as adrenaline. This can trigger an immediate increase in the heart rate.
- The body is fighting illness or fever: When you are fighting illness or suffering from fever and the heart rate may increase due to higher metabolic demands and also the body’s effort to control the body’s temperature.
- Drugs and substances: Certain drugs like beta-blockers, or asthma medication, can cause Tachycardia as a side effect. In addition, certain substances like nicotine, caffeine alcohol, caffeine, and other illicit substances can be a factor in an increased heart rate.
- Medical conditions:
- Heart-related diseases: Certain heart conditions, including coronary artery disease and heart failure, valve issues or congenital heart defects and irregularities within its electrical system, can all increase heartbeat frequency significantly.
- Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid can increase metabolic processes in your body and result in faster heart rates.
- Anemia: A lower number of red blood cells or a decrease in hemoglobin levels could cause a compensatory rise in heart rate, which helps to supply increased oxygenation to tissue.
- Pulmonary embolism: Pulmonary Embolism occurs when a blood clot forms in your lungs that block circulation, prompting your heart to pump more Quickly to compensate.
- Other medical conditions: Other medical conditions, including high blood pressure and electrolyte imbalances, May contribute to tachycardia Including Sepsis or Tumors.
Noting the list here does not constitute a definitive examination; in order to accurately diagnose tachycardia in any one instance, consulting with a doctor and having them perform a comprehensive physical is vitally necessary.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Tachycardia
Tachycardia symptoms vary based on its cause and severity as well as individual circumstances; symptoms commonly seen Include:
- A rapid heartbeat: An early indicator of tachycardia may include experiencing an elevated heart rate above their regular resting heart rate and/or feeling their heart Racing.
- Breathlessness: Tachycardia can cause inadequate blood flow to the body which can cause a feeling of breathlessness or breathing difficulty, particularly during exercise or other sports.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: An increase in heart rate could obstruct blood from reaching the brain, potentially leading to lightheadedness, Dizziness, or Fainting Symptoms.
- Chest discomfort or pain: People suffering from tachycardia often report feeling discomfort or pain in the chest area; it should also be remembered that chest discomfort could signal something more serious, like an attack on your heart; therefore seeking medical advice as soon as possible to diagnose its source.
- Insomnia and fatigue: Tachycardia may result in diminished cardiac output and weakening, fatigue or an overall sense of low energy and Tiredness.
Diagnose Tachycardia:
Healthcare professionals can administer various tests and diagnostics to diagnose tachycardia. For instance:
- Physical examination: Healthcare providers will assess a patient’s blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital Indicators. They’ll also ask about any conditions or medical history as well as medications or substances which might contribute to tachycardia.
- Electrocardiogram: The non-invasive test measures the heart’s electrical activity and may help to detect abnormal heart rhythms that are associated with Tachycardia.
- Holter Monitor: The small gadget is worn by an person for a period of 24 to 48 hours to capture indefinite ECG readings. It is able to record instances of tachycardia, which might not be detected in the normal ECG.
- Event monitor: Like an Holter monitor Event monitors are employed for longer periods of time as well as activated by an individual when they feel ill. This allows for a targeted ECG recordings during tachycardia episodes.
- Tests for blood: These tests can be carried out to identify underlying issues like thyroid issues electrolyte imbalances, other causes that could be causing tachycardia.
- Echocardiogram: The procedure utilizes ultrasound to generate images of the heart’s structure as well as function. It helps to identify heart problems or structural issues that could cause tachycardia.
In certain instances, specific tests or consultation with cardiac specialists might be needed to determine the exact causes of Tachycardia. If a diagnosis is established the appropriate treatment options will be discussed, and then implemented in order to manage the issue effectively.
Treatment Options for Tachycardia
The options for treating Tachycardia vary based on the reason, severity of the symptoms, and individual variables. The aim in treatment is to restore healthy heart rhythm, relieve symptoms, and lower the chance of complications.
Here are some typical treatment options for tachycardia:
- Vagal movements: They are easy methods that activate the vagus nerve and reduce heart rate. Examples include slowing down like you’re experiencing an intestinal movement by coughing hard or soaking one’s face with cold water. Vagal exercises are commonly employed for specific types of supraventricular tachycardia.
- Medicines: Antiarrhythmic medication may provide relief for Tachycardia symptoms. Your choice will depend on its form as well as other aspects. These drugs regulate electrical signals generated by the heart or decrease heart beat rate by slowing it down – some examples being beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers as well as antiarrhythmic medicines.
- Cardioversion: In the case of tachycardia where medications or vagal exercises aren’t effective, a cardioversion procedure can be administered. It involves the delivery of an electric shock that is controlled to the heart to reestablish an normal heart rhythm. It can be performed as either an electrical cardioversion (using electrodes) or an pharmacological cardioversion (using drugs).
- Catheter ablation: Catheter ablation is a minimally-invasive procedure carried out by an electrophysiologist for cardiac purposes. It involves the placement of a catheter inside the heart to find and remove the abnormal electrical pathways that trigger tachycardia. The use of cryoablation or radiofrequency energy could be utilized to eliminate the target tissue that is responsible for the irregular rhythm.
- Implantable devices: For specific kinds of tachycardia difficult to treat with medication as well as ablation techniques, the use of implantable devices could be suggested. These devices include implantable cardioverter-defibrillators or pacemakers that track and regulate heart Rhythm.
- Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes may help alleviate tachycardia symptoms and limit its frequency or intensity of episodes. This could include the avoidance of triggers like stimulants or caffeine as well as managing stress levels with therapies or relaxation techniques and maintaining an appropriate weight exercise routine, and avoid drinking too much alcohol.
It’s crucial to understand that the treatment method is determined by a health expert based on the patient’s particular circumstance. Treatment decisions could also depend on other considerations, including any existing heart conditions and frequency and length of episodes associated with tachycardia; as well as general health considerations. Regular follow up visits and continuous monitoring must take place to evaluate effectiveness.
Definition of Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a medical condition defined by an abnormally slow heartbeat. People living with bradycardia experience heartbeats that fall less than the typical pace, typically 60 to 100 beats per minute; though its precise threshold varies based on factors including age and overall health status.
Low heart rates can compromise the body’s capacity to absorb sufficient quantities of blood from your heart, potentially leading to complications or symptoms that need treating in order to ensure overall good health and heart function. It’s therefore imperative that bradycardia be detected and managed, in order to keep cardiovascular systems working efficiently for overall good health and prevent potential future issues with health-related conditions such as hypertension.
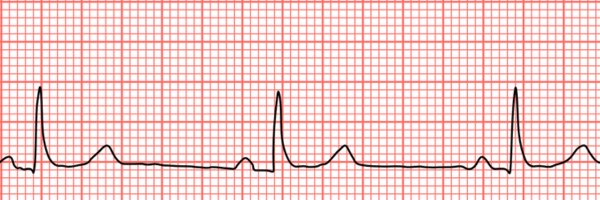
Bradycardia refers to any state in which electrical impulses from your heart’s primary rhythm generator, the sinus node, are generated at lower than usual speeds compared to what would typically occur. Other forms include heart block where electrical signals between lower and upper chambers are either blocked or delayed and sick sinus syndrome which produces irregular heartbeats.
Bradycardia can occur for various reasons. Some individuals may simply be born with slow heart rates without experiencing symptoms; or bradycardia could result from medical conditions like hypothyroidism, heart disease or electrolyte imbalances as a side-effect of medications taken; it could even stem from genetics, age or lifestyle choices like excessive endurance exercise or substance use as contributing factors in developing bradycardia.
Reaching out to healthcare providers in order to accurately diagnose and treat bradycardia can be essential in providing accurate diagnoses and effective solutions. Healthcare practitioners will assess medical history, conduct physical exams on patients and perform diagnostic tests like Electrocardiogram (ECG). ECG tests monitor electrical activity within the heart and identify its rate.
Treatment strategies for bradycardia vary based on its source and symptoms severity as well as overall patient health status. Treatment may not always be necessary if symptoms are mild; in such instances lifestyle changes, medication to regulate heart rate or medical procedures like pacemaker implantation could provide solutions that restore normal rhythm while improving overall heart function can all help address bradycardia issues.
Patients diagnosed with bradycardia must work closely with medical professionals in developing an appropriate treatment plan and receiving regular check-ups in order to maintain optimal heart health and prolong a full and active lifestyle while decreasing risks of future medical issues. With proper bradycardia care plans in place, people can lead an extended and healthy existence free from problems that threaten long-term living.
Causes of Bradycardia
Bradycardia is a disorder characterized by a heart rate that is slower than normal usually described as a heart rate lower than 60 beats per min in adults.
There are many possibilities for bradycardia to be the cause, such as:
- Ageing: As people get older, their heart’s natural pacemaker, known as the sinoatrial (SA) node, could perform less effectively and result in a lower heart rate.
- Medicines: Certain medications like beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers could reduce heart rates as a result. These antiarrhythmic medicines could include beta-blockers and calcium channel Blockers.
- Conditions of the heart: A variety of heart diseases can cause disruption to those electrical pulses which regulate heart rate and cause bradycardia. Examples include.
- Sinusitis: The disorder happens due to the fact that the SA node fails to function properly, resulting in an insuficient heart rate or periods of intermittent bradycardia and the tachycardia.
- Heart block: Slow heart rate results when electrical signals from the atria fail to reach the ventricles efficiently and cause an irregular heart Rhythm.
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack): An attack can alter an electrical transmission system of your heart muscle and lead to its weakening; this in turn may trigger bradycardia.
- Cardiomyopathy: Sickle cell anemia refers to any condition affecting cardiac muscle that decreases its effectiveness at pumping blood, potentially leading to bradycardia or its symptoms.
- Hypothyroidism: The inactivity of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) could result in slowing heart rate because of a lower levels of hormones thyroid which regulate heart function and metabolism.
- Certain infections: Endocarditis infection of the heart’s inner lining and myocarditis inflammatory condition of heart muscle can alter its electrical circuit and cause bradycardia, or slow heart rate.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: A condition that by breath pauses while you sleep, may cause bradycardia because of decreased oxygen levels and an increased strain to the heart.
- Conditions of the nervous system: Certain neurological conditions, like autonomic dysfunction and some types of stroke, may interfere with normal heart regulation processes and cause bradycardia to set in, leading to irregularly slow heart rates that result in Bradycardia.
- Certain lifestyle issues: Certain lifestyle factors, such as excessive exercise, specifically endurance sports, could cause bradycardia when the heart adjusts to demands of intensive training. In addition, extreme malnutrition or electrolyte imbalances can cause heart dysfunction and contribute to bradycardia.
As it should not always require treatment, bradycardia shouldn’t always necessitate medical intervention when nonsymptomatic and mild. But if symptoms of dizziness fatigue fainting or breathing issues arise as well as any potential links with heart conditions then medical evaluation and treatment could become necessary. Healthcare professionals would evaluate medical history along with conducting physical exams and running diagnostic tests to pinpoint the source of problem before creating personalized plans to tackle any issues identified during evaluation and treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Bradycardia
The symptoms of Bradycardia, which is an increased heart rate than normal and isn’t always associated with obvious symptoms, particularly when the heart rate is within a normal range and doesn’t significantly impact the flow of blood. When the bradycardia condition becomes more prominent or results in insufficient blood flow,
people might experience the following signs:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or depleted of energy, even when doing only physical effort is a frequent sign of bradycardia.
- Lightheadedness or dizziness: A decrease in circulation of blood to brain may create feelings of dizziness, lightheadedness or even fainting.
- Breathlessness: Insufficient blood flow can cause breathing difficulties or breathlessness especially during physical exercise.
- Pain or discomfort in the chest: Bradycardia sufferers may feel chest pain. This may vary in the intensity and duration. Keep in mind that chest pain could be an indicator of more serious illnesses like a heart attack; therefore an immediate medical examination is recommended.
- Trouble with cognitive or confusion: A lack of circulation of blood to the brain could result in mental confusion, fog or problems in memory and concentration.
- Cold extremities or pale skin: The reduced circulation of blood can trigger changes in the color of skin and temperature, which can lead to cold or pale extremities.
The diagnosis of Bradycardia: The identification of bradycardia is based on a thorough medical examination by a healthcare expert. Below are several diagnostic procedures and tests which may be employed:
- Physical examination and medical history: The doctor will inquire into symptoms such as medical history, lifestyle choices and medications taken. A physical exam may also be undertaken in order to detect vital signs such as blood pressure and heart Rate.
- Electrocardiogram: Monitoring heart electrical activity helps diagnose bradycardia by showing an elevated heartbeat rate compared with that of normal.
- Holter monitors: These small monitor is worn by an individual for between 24 and 48 hours to capture indefinite ECG readings. It is able to record occasional moments of bradycardia which may not be identified during an ordinary ECG.
- Event monitor: Event monitor similar to the Holter monitor Event monitors are utilized for longer durations as well as activated by an individual when they feel symptoms. This permits for specific ECG recordings during bradycardia episodes.
- Echocardiogram: The test makes use of ultrasound to produce images of the structure and function. It helps to identify any structural problems that are underlying, or heart-related conditions that cause bradycardia.
- Stress test for exercise: In some instances the exercise stress test could be used to test the heart rate response in exercise, and also to check for bradycardia caused by Exercise.
- Blood tests: Blood tests could help identify some underlying conditions, including thyroid or electrolyte imbalances. These can cause bradycardia.
Diagnostic procedures aim to discover the cause and develop the most appropriate strategy to treat bradycardia. If the symptoms are serious or have been associated with health risk seeking medical attention immediately is essential to manage the problem and avoid complications.
Treatment Options for Bradycardia
Treatment options for bradycardia – which refers to any condition wherein one experiences slower heart rates – depend on its cause, severity of symptoms and individual circumstances. Treatment aims at alleviating discomfort as well as improving circulation to reduce complications; below are a few popular treatment approaches for bradycardia.
- Observation and monitoring: Monitoring and observation in certain instances when bradycardia appears mild and not symptomatic, careful observation and monitoring could suffice. Regular follow-up visits with a medical professional could assist in assessing the heart rate and assess any changes or changes.
- Medicines: Medications can be used to increase heart rate or to improve the heart rhythm. Examples include:
- Atropine: Atropine is an anti-inflammatory medicine which temporarily increases heart rate by suppressing vagus nerve activity.
- Pacemaker: It is an implanted device under the skin, often inside the chest, in order to regulate heart rate. It sends electrical impulses to the heart whenever needed to ensure a healthy heart rate.
- Lifestyle changes: Certain lifestyle modifications can aid in reducing bradycardia and improving the condition of your heart. They could include:
- Beware of excessive drinking: Drinking excessively can cause irregular heartbeats and may cause bradycardia.
- Quitting smoking: Being healthy and maintaining a weight Overweight and obesity cause strain on the heart and lead to bradycardia.
- Stop smoking cigarettes: Smoking cigarettes can have detrimental effects on both cardiovascular systems and increase risk for certain heart disorders like bradycardia.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity under the supervision by a medical professional, can aid in improving cardiovascular health and improve heart rate.
- Treating underlying medical conditions: Treatment of medical conditions that are underlying Bradycardia can be due to an underlying medical condition like hypothyroidism, or a heart blockage Treating the condition could help to improve the rate of heartbeat.
- Surgery: In some situations, surgery may be required to treat bradycardia. This may be done through procedures such as:
- The implantation of pacemakers: As mentioned previously, implanting a pacemaker could help regulate heart rate and ensure adequate electrical signaling.
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy: Cardiac resynchronization therapy involves the installation of specific pacemakers to regulate the heart’s contraction chambers, and to improve the performance of the heart.
Treatment options for bradycardia – which refers to any condition wherein one experiences slower heart rates – depend on its cause, severity of symptoms and individual circumstances. Treatment aims at alleviating discomfort as well as improving circulation to reduce complications; below are a few popular treatment approaches for bradycardia.
Differences between Tachycardia and Bradycardia
Tachycardia and bradycardia, two separate disorders which refer to irregularities in heartbeat rate, differ significantly in several aspects;
Here are the key distinctions:
Definition:
- Tachycardia: It is typically defined as a heart beat that exceeds 100 beats per minute for adults who are at rest.
- Bradycardia: Bradycardia, on the contrary, refers to the heart’s rate being slower than normal. It’s typically described as a heart rate lower than 60 beats per minute for adults who are at rest.
Heart Rate:
- Tachycardia: The rate of the heart in tachycardia can be high, which is above that of normal. This could result in the heart beating rapidly or racing.
- Bradycardia: A heartbeat in bradycardia can be slower than normal range. This can result in an irregular or slow heartbeat.
Causes:
- Tachycardia:Tachycardia may result from various sources, including physical exertion, emotional strain, and fever; hormone Imbalances, Medications, heart-related conditions like atrial fibrillation or ventricular Tachycardia, and Medical ailments that cause Irregular Heartbeats.
- Bradycardia: Bradycardia can result due to aging, certain drugs (e.g. beta-blockers, beta-blockers) or heart-related conditions (e.g. heart block and sick sinus syndrome) or hypothyroidism, infection and neurological disorders or an normal physiological change for athletes who have been trained to the highest level.
Symptoms:
- Tachycardia: Signs and symptoms of tachycardia include rapid heartbeat or palpitations; shortness of breath; dizziness chest discomfort lightheadedness fatigue & fainting are other possible outcomes of this disorder.
- Bradycardia: The symptoms of bradycardia can include fatigue, dizziness shortness of breath, lightheadedness discomfort or chest pain and confusion, fainting and cold extremities.
Diagnosis:
- Tachycardia: Tachycardia can be diagnosed by reviewing symptoms and medical histories, conducting physical exams and running diagnostic tests such as electrocardiography (ECG), Holter monitor test for blood, event monitor and echocardiography.
- Bradycardia: Bradycardia can be diagnosed by a similar method of taking a look at the symptoms such as medical history, physical exam and diagnostic tests like ECG, Holter monitor, event monitor, blood tests and echocardiogram.
Treatment:
- Tachycardia: Treatment options for tachycardia include vagal maneuvers and medications (e.g. beta-blockers calcium channel blockers) as well as cardioversion, catheter ablation implantsable medical devices (e.g. pacemakers, pacemakers, defibrillators) as well as lifestyle changes.
- Bradycardia: Bradycardia treatment options could consist of observation, medications (e.g. atropine) or pacemaker implantation dealing with medical conditions that cause the condition or lifestyle changes as well as, in some instances surgical interventions.
It’s crucial to understand that the treatment and management for bradycardia and tachycardia is contingent on the root reason, the degree of symptoms, as well as the individual circumstances. So, a medical expert’s assessment and advice are crucial for a an accurate assessment and diagnosis.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment Options for Tachycardia:
- Vagal maneuvers: Vagal maneuvers are methods that stimulate the vagus nervous system to slow down the rate of heart. Examples include slowing down like you’re having an intestinal motion, coughing vigorously or submerging your face in ice cold water.
- Medications: Antiarrhythmic medicines or beta-blockers could also help decrease heart rates during times of tachycardia. Other specific solutions could also include calcium channel blockers.
- Cardioversion: If the tachycardia continues to occur and doesn’t be responsive to treatments other than that, a cardioversion procedure may be thought of. It involves administering an electric shock controlled into the heart to bring it back to the normal rhythm.
- Catheter ablation: Catheter ablation involves threading flexible, thin tubing (catheters) into blood vessels and into the heart. The catheters emit high-frequency radiofrequency or extremely cold to kill those abnormal tissues of the heart that is responsible for tachycardia.
- Implantable devices: Implantable devices like pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators may be recommended in certain Instances. Pacemakers regulate heart rate, and ICDs can be used to identify and treat arrhythmias that could be life-threatening.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Making lifestyle modifications can aid in managing tachycardia, and help reduce its severity and frequency. It could be as simple as eliminating triggers such as caffeine, stress, alcohol and nicotine, ensuring the weight of a healthy person regular exercise routine, managing chronic medical conditions and the reduction of stress levels.
Treatment Strategies for Bradycardia
- Monitoring and observation: In the event that bradycardia is not severe and unaffected, regular monitoring by a medical professional could suffice. The heart rate of the patient and signs will be carefully watched to ensure that there are there aren’t any complications.
- Treatments: When bradycardia triggers symptoms or is an risk to the person’s health, drugs like atropine could be used to raise the heart rate for a short period of time. Other medications may also be available for the treatment of bradycardia-causing Conditions.
- Pacemaker Implantation: A pacemaker tiny electronic device placed under the skin, mostly within the chest. It regulates your heart’s rate through sending electric signals to the heart when needed. They are often used in those with bradycardia that is significant or heart blockage.
- Treating underlying conditions: Treatment of underlying issues If the cause of bradycardia is due to an underlying problem like hypothyroidism, or other heart-related conditions Treating the root causes can help restore a healthy heartbeat.
- Lifestyle changes: Similar to tachycardia and other heart conditions, certain lifestyle adjustments are beneficial to people suffering from bradycardia. It could be as simple as abstaining from drinking alcohol excessively and keeping healthy weight, avoiding smoking cigarettes, and engaging regularly in exercise under the supervision of a medical expert.
Understanding that treatment strategies for bradycardia and tachycardia will depend upon factors like root causes, severity of symptoms and specific aspects is of critical importance in providing appropriate remedies. Therefore, it’s essential to speak with a healthcare expert for a precise diagnosis and a customized treatment strategy.
Conclusion
Understanding abnormal heart rhythms like tachycardia and bradycardia is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. Proper diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions. If you experience any unusual symptoms related to your heart rate, seek medical attention promptly.