Syphilis and Gonorrhea are distinct sexually transmitted infections (STIs) caused by different bacteria. Syphilis, caused by Treponema pallidum, progresses through stages and can have severe complications if untreated. Gonorrhea, caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, typically presents with localized symptoms and can lead to complications but is treatable with antibiotics.
What is Syphilis?
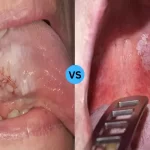
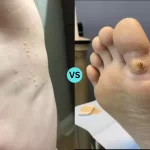
Syphilis can be described as a sexually transmitted illness (STI) that is caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum. It’s usually transmitted via sexual contact, such as vaginal, anal, or oral sexual contact. If left untreated, this infection progresses through distinct stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary.
Each stage presents different symptoms and can have varying effects on the body. Syphilis is diagnosed through blood tests and can be treated with antibiotics, especially in its early stages, to prevent complications that may affect the heart, brain, nerves, and other organs.
What is Gonorrhea?
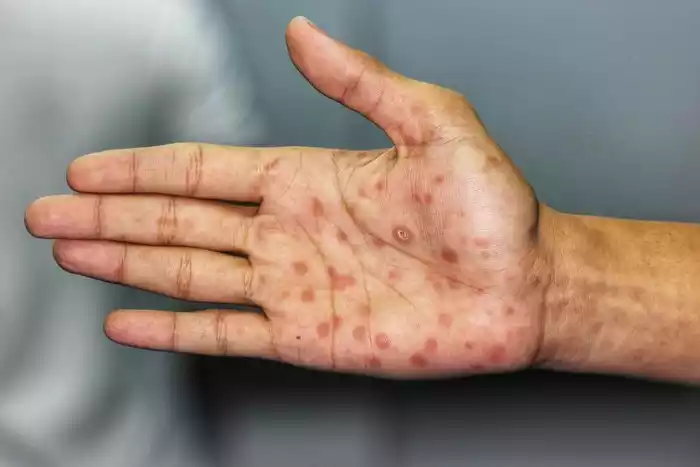
Gonorrhea is an infection that is transmitted sexually (STI) and is caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It primarily spreads through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected individual. This infection can affect the genitals, rectum, and throat. Symptoms of gonorrhea include pain during urination, abnormal genital discharge, and, in some cases, no noticeable symptoms.
If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to serious complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (in women), infertility, and an increased risk of contracting HIV. Diagnosis involves testing urine samples, genital swabs, or other bodily fluids, and treatment typically involves antibiotics to cure the infection. Regular testing and safe sexual practices are crucial in preventing the spread of gonorrhea.
Importance of understanding specific STIs: Syphilis and Gonorrhea
Knowing the difference between gonorrhea and syphilis is vital due to their distinctive characteristics and health risks. Syphilis, as it progresses through stages, could cause severe complications if left untreated while gonorrhea with specific symptoms, could cause complications, but it can be treated.
Understanding the differences in symptoms stages, treatment, and symptoms aids in the early detection, effective treatment, and prevention of chronic health problems, highlighting the importance of specific health awareness and initiatives.
Comparison chart of Syphilis and Gonorrhea
Here’s a comparison chart highlighting the key differences between syphilis and gonorrhea:
| Characteristics | Syphilis | Gonorrhea |
| Causative Agent | Treponema pallidum | Neisseria gonorrhoeae |
| Transmission | Sexual contact (vaginal, anal, oral) with an infected person | Sexual contact (vaginal, anal, oral) with an infected person |
| Stages | Primary, secondary, latent, tertiary | Typically presents with acute infection |
| Progression | Progressive stages, each with specific symptoms and manifestations | May show localized symptoms or asymptomatic |
| Symptoms | Sores or ulcers (primary stage), rash, fever (secondary stage), latent stage often asymptomatic, tertiary stage involves severe complications | Painful urination, abnormal genital discharge, rectal infections, throat infections; can be asymptomatic |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests (RPR, VDRL), sometimes with confirmation via specific treponemal tests | Testing of urine samples, genital/rectal swabs, throat swabs |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (penicillin, doxycycline) based on the stage | Antibiotics (cephalosporins, azithromycin) |
| Complications | Can affect the heart, brain, nerves, and other organs if untreated | Can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, and increased risk of HIV if untreated |
Prevention and Public Health Perspectives
Preventing the spread of syphilis and gonorrhea involves various public health strategies and individual measures. Public health initiatives focus on education, awareness campaigns, and access to healthcare services. These programs aim to inform communities about safe sexual practices, the importance of regular STI testing, and the availability of treatment options.
Individual prevention starts with practicing safe sex, which includes consistent and correct use of condoms during sexual activity. Regular STI testing, particularly for individuals with multiple sexual partners or engaging in unprotected sex, is crucial for early detection and timely treatment. Partner notification and contact tracing are also essential aspects of preventing further transmission. It involves informing sexual partners of an individual diagnosed with an STI to encourage their testing and treatment, thereby breaking the chain of infection.
Furthermore, vaccination research and development play a significant role in preventing STIs like HPV, which can cause complications like genital warts and certain cancers. Encouraging vaccination against specific STIs where available contributes to overall community immunity and reduces the spread of infections.
In essence, a combination of public health interventions focusing on education, accessible healthcare, and individual efforts in practicing safe sex and seeking timely medical care is key to preventing the transmission and reducing the impact of syphilis, gonorrhea, and other sexually transmitted infections.
What are the symptoms of Syphilis and Gonorrhea?
Here are the summarized symptoms of syphilis and gonorrhea:
Syphilis Symptoms
- Primary Stage: One or more painless sores (chancre) on the genitals, rectum, or mouth.
- Secondary Stage: Skin rash, mucous membrane lesions, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and other flu-like symptoms.
- Latent Stage: Asymptomatic (no visible symptoms).
- Tertiary Stage: Severe complications affecting various organs, potentially leading to heart problems, paralysis, blindness, and dementia.
Gonorrhea Symptoms
- Men: Painful or burning sensation during urination, abnormal discharge from the penis, swollen or painful testicles.
- Women: Painful urination, increased vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, pelvic pain.
- Both: Rectal infections may cause discharge, itching, and bleeding, and throat infections might result in a sore throat.
It’s important to note that both syphilis and gonorrhea can also be asymptomatic, particularly in the early stages. Regular testing and seeking medical advice if engaging in risky sexual behavior or experiencing any concerning symptoms are crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Knowing the distinctions between syphilis and gonorrhea is essential for effective treatment and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STIs). Syphilis is a progressive disease that can occur in different stages and can lead to serious complications if not treated and gonorrhea typically presents with symptoms that are localized and may result in complications, but is treated by using antibiotics.
A timely detection, regular tests, practicing safe sexual activity, and seeking prompt medical attention are crucial to keeping these STIs and maintaining good sexual health.