Overview of System Approach and System Analysis
System Approach: The System Approach is an integrative and interdisciplinary method for comprehending complex systems. It requires viewing them as wholes rather than individual pieces; acknowledging interdependencies among them and any interplay among their parts; considering context, boundaries, behaviors, and performances when approaching these processes; and understanding that changes to one part may cause ripple effects through others in a system.
Key characteristics of system approaches:
- Holistic perspective: It takes a holistic view of a system and emphasizes its interrelationships among its components. Interconnections and
- Interdependencies: It acknowledges that components within any given system have interdependent relationships that affect their behavior.
- System Boundaries: This task seeks to define the boundaries of a system by specifying its inclusion or exclusion criteria from consideration. System Behavior and Performance: Here, the emphasis lies on understanding its dynamic performance over time.
- Contextual understanding: It requires taking into account external influences and environmental conditions which impact on a system, along with feedback-driven observations, analyses and adaptation based on system feedback.
- Iterative and feedback-driven: These processes involve iterative cycles of observation, analysis and adaptation based on feedback from within a system itself.
- Application of System Approach: The System Approach can be found across many fields such as management, engineering, biology, social sciences and environmental studies. It assists practitioners with comprehending complex problems more readily while designing efficient solutions and overseeing complex systems more successfully. System thinking models often serve to analyze and enhance system performance as part of this approach.
- System Analysis: System analysis is one component of the broad system approach and serves to understand, evaluate and improve systems through systematic approaches and processes. System analysis utilizes various techniques and tools for identification problems as well as collecting relevant data on system objectives and constraints to develop models of them to evaluate different solutions before finally implementing and monitoring any chosen ones.
Key components of system analysis:
- Problem Identification and Definition: Accurately identifying the issue or opportunity which requires analysis and improvement, along with gathering relevant data such as inputs, processes outputs feedback. Incorporation and Analysis: Collecting relevant information such as inputs processes outputs feedback as the current state of your system to support analysis of existing system issues
Identification of System Objectives and Constraints: Establishing desired goals and limitations of the system. - System Model Creation: Crafting models which represent its structure, behavior and interactions in detail.
Evaluating Alternative Solutions: Assessing different options and their potential effects on the system.
Implementation and Monitoring the Selected Solution: Initiate implementation and continuously assess its performance over time.
Tools and Techniques Employed in System Analysis: System analysis employs numerous tools and techniques that assist the analysis process, such as interviews, surveys, observations, data flow diagrams/flowcharts/flowcharts as well as system dynamics modeling/simulation tools/and optimization techniques to aid its evaluation process. - Importance of system analysis: System analysis can play an integral part in decision-making and problem-solving for organizations. By mapping complex relationships within systems, understanding inefficiencies or bottlenecks more clearly, and developing effective solutions. System analysis helps organizations make informed decisions, enhance processes, optimize resource allocation more efficiently, and ultimately increase overall system performance.
- Relationship Between System Approach and Analysis: System analysis is one method employed within the greater framework of system approach. While system approach emphasizes understanding systems holistically, system analysis uses its principles and concepts as guidance in analyzing specific systems within that broader context. System approach uses principles from system analysis as its base methodology so as to ensure an holistic perspective when studying any given system under consideration.
The systems approach and analysis are complementary concepts designed to understand, manage and optimize complex systems. While system analysis offers systematic methods of improving individual components within that broader framework. Both concepts play a crucial role in providing insights for improving complex systems.
Importance of understanding systems in various fields
Understanding systems is of vital importance in many fields for several reasons, including:
- Problem Solving: Systems thinking enables professionals to approach problems from an holistic viewpoint. By understanding interactions and interdependencies within systems, individuals can identify root causes more easily while devising lasting solutions which address root issues rather than treating symptoms only.
- Efficiency and Optimization: Systems thinking allows professionals to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks and opportunities for improvement within any system. By studying inputs, processes, outputs and resource allocation patterns professionals can optimize system performance while decreasing wasteful spending while increasing resource allocation resulting in enhanced efficiency and productivity.
- Risk Management: Systems Thinking can assist professionals in recognizing potential risks and their effects on systems as a whole, helping professionals anticipate and mitigate threats before they escalate, thus mitigating negative repercussions and mitigating risk before it escalates into greater negatives consequences.
- Innovation and design: Systems thinking encourages an inventive and imaginative approach to problem-solving, providing professionals with opportunities for imagination and inventive approaches that tackle system’s complex issues with unique solutions. It allows professionals to visualize new scenarios while considering alternative perspectives before developing novel answers that address complex system’s obstacles and difficulties.
- Collaboration and teamwork: Systems thinking fosters cooperation and multidisciplinary approaches, providing professionals from different fields the chance to pool their diverse expertise to solve difficult problems and reach shared objectives more efficiently.
- Adaptability and resilience: Systems are dynamic entities, constantly shifting. Understanding these dynamic environments enables individuals and organizations to adapt quickly to changes, anticipate future trends, and build resilience. Recognizing feedback loops and system behavior enable professionals to respond swiftly in changing circumstances by altering strategies proactively or altering strategies as circumstances dictate.
- Sustainability and long-term planning: Systems thinking is integral for sustainability efforts and long-term planning, enabling professionals to consider all environmental, social, and economic ramifications of their decisions and design sustainable strategies that support long-term viability.
- Policy Development and Implementation: Systems understanding is fundamental in policy creation and implementation. Policies must take into account their wider impact, account for any unintended outcomes and aim at systemic solutions rather than isolated fixes.
- Healthcare and medicine: Understanding the human body as an interdependent system is integral to accurate diagnosis, effective treatment and preventive healthcare services. Systems thinking provides healthcare providers a tool to identify contributing factors for any issues within patient health conditions as well as devising comprehensive approaches to patient care.
- Business Management: Systems Thinking can play an invaluable role in business management, helping leaders examine the organization as an interrelated system to optimize processes, enhance decision-making processes and boost overall performance. Furthermore, systems thinking allows managers to identify relationships among departments, stakeholders and market factors for more informed strategies to be created by management teams.
Understanding systems is critical across various fields, as it enhances problem-solving, efficiency, risk management, innovation collaboration adaptability sustainability policy development healthcare management business management among other functions. By adopting an understanding systems perspective professionals can navigate complex challenges more successfully while making positive, lasting change to their respective areas of influence.
System Approach
System Approach refers to an holistic, multidisciplinary approach for understanding and managing complex systems. It involves viewing systems as wholes rather than its individual parts; acknowledging interdependencies among them as well as interrelations among them all; considering context, boundaries, behavior, and performance aspects as necessary when making decisions for effective system administration.
Key characteristics of the System Approach include:
- Holistic Approach: When approaching systems holistically, their components and interactions must all be taken into consideration to gain an accurate picture. Analysis of individual parts alone cannot reveal all that makes up their behavior and performance as one entity.
- Interconnections and Interdependencies: The system approach emphasizes the interrelations and dependencies among components within a system, noting how changes to one component could have far reaching effects throughout other areas. Acknowledging and understanding these relationships is fundamental in grasping its entirety.
- System Boundaries: When approaching any system, one important aspect is defining its boundaries in terms of what should and shouldn’t be included within. This helps demarcate its scope for analysis as well as understanding relationships between it and its surroundings.
- System Behavior and Performance: The system approach emphasizes an in-depth examination of a system’s dynamic behavior and performance over time, such as responding to inputs, processing them effectively and producing outputs; adapting and evolving in response to changes in its environment and changing conditions.
- Contextual Understanding: A system approach takes into account external influences that have an effect on its operation and performance, including external factors and environmental conditions that a system must deal with. The approach acknowledges that systems exist within larger contexts that influence both their behavior and performance outside their immediate borders.
- An Iterative and Feedback-Driven Approach: The system approach takes an iterative approach that involves ongoing observation, analysis and adaptation based on feedback from the system itself. It recognizes that systems can be complex and dynamic entities which requires regular adjustments for desired results to occur.
The system approach finds applications across many disciplines, from management and engineering to biology and environmental studies. It helps in comprehending complex problems quickly while offering effective solutions, managing complex systems efficiently. Furthermore, system thinking models such as System Dynamics may also be employed to analyze performance improvements of systems.
The system approach offers a holistic framework for comprehending and managing systems by considering their holistic nature, interconnections, behavior and performance. This methodology empowers professionals to take an in-depth view of complex systems while making more informed decisions that lead to desired results within them.
System Analysis
System Analysis is an organized and systematic practice of understanding, evaluating and improving systems. This involves employing various techniques and tools to study its components, interactions and behavior so as to detect issues, propose solutions and optimize system performance.

Key components of System Analysis include:
- Problem Identification and Definition: Accurately identifying a challenge or opportunity that needs analyzing or improving, by understanding goals, constraints and challenges of your system.
- Gathering and Analyzing Relevant Data: Collecting relevant information regarding the system’s current state – this includes inputs, processes, outputs, feedback loops and customer comments – may involve interviews, surveys or observations as data collection methods in order to gain qualitative and quantitative data for analysis.
- Establishing the Objectives and Constraints of the System: Establishing desired goals and limitations helps define criteria against which alternative solutions will be evaluated.
- Develop System Models: Constructing models that accurately depict a system’s structure, behavior and interactions is one approach for visualizing and analyzing it. Tools like flowcharts, data flow diagrams and system dynamics models may all help illustrate and assess systems more thoroughly.
- Evaluation of Alternative Solutions: Examining different options and their potential effects on a system involves weighing their advantages, disadvantages, risks, feasibility and selection process to find one which most fits.
- Implementation and Tracking the Selected Solution: After choosing an optimal solution, its implementation must be monitored continuously in order to assess its efficacy, identify areas for enhancement, and make any required modifications or alterations.
System Analysis utilizes numerous tools and techniques, such as:
- Data Collection Methods: Interviews, surveys, observations and document analysis can all be employed as data gathering techniques in the collection process of system related information.
- Modeling Techniques: In order to represent and analyze systems effectively, various modeling techniques such as flowcharts, data flow diagrams, entity relationship diagrams, system dynamics models and simulation tools may be utilized as modeling approaches.
- Simulation and Optimization Tools: Simulation tools enable the evaluation and testing of various scenarios or alternatives within a system while optimization techniques help find optimal solutions by either increasing performance or decreasing costs.
System Analysis is essential to making sound decisions and finding effective solutions in various domains. By understanding complex relationships within systems, identifying inefficiencies or bottlenecks and developing appropriate remedies, System Analysis allows organizations to make more informed decisions, optimize process performance, maximize resource allocation efficiency and boost overall system performance.
System Analysis helps organizations understand, assess and improve systems through employing systematic methods and using various tools; this leads to more efficient operations, improved decision-making capabilities and efficient problem-solving techniques.
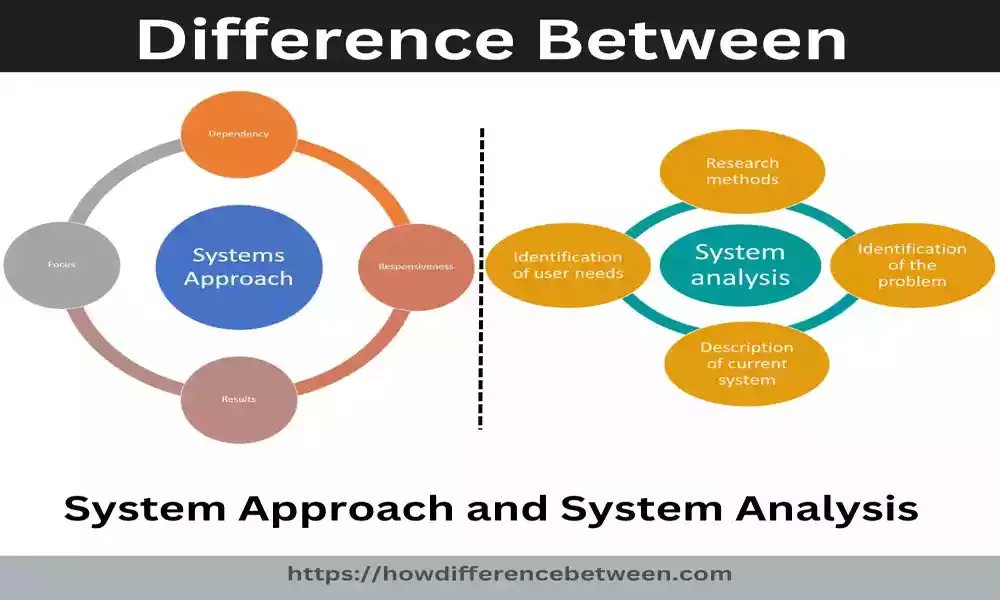
Comparison between System Approach and System Analysis
Comparison Between System Approach and Analysis:
Definition of System Approach:
- System Approach: A system approach is an integrative and multidisciplinary method for understanding and overseeing complex systems, emphasizing taking an holistic view and acknowledging any interdependencies or interactions among its components.
- System Analysis: System analysis is one component of system approach; it involves conducting systematic and structured processes designed to evaluate, understand and enhance systems using various techniques and tools.
Scope and Focus:
- System Approach: This approach to complex systems provides an overall perspective for understanding and controlling them effectively, taking into account aspects such as context, boundaries, behavior and performance of its constituent parts as a whole system. It recognizes interdependency of components.
- System Analysis: System analysis entails conducting detailed investigations on specific systems within a broader system approach framework, in order to identify issues, collect and analyse data, build models to test potential solutions and implement and monitor those chosen solutions for that system under study.
Methodology:
- System Approach: This framework and set of principles provide a conceptual foundation and set of rules for understanding systems holistically from multiple points of view and perspectives, such as interconnectivities and contextual aspects of systems.
- System Analysis: System analysis provides a systematic and structured methodology for examining and improving systems, which includes steps such as problem identification, data gathering/analysis/modelling development/evaluation and implementation.
Application:
- System Approach: This methodology finds application in various fields such as management, engineering, biology, social sciences and environmental studies to understand complex problems more thoroughly, design effective solutions and manage complex systems more successfully.
- System Analysis: System analysis falls within the general system approach framework and serves to examine and improve specific systems within various domains such as business processes, information systems, healthcare platforms or transportation infrastructures.
Relationship:
- System Approach: System Approach and System Analysis are inextricably linked concepts; system analysis being one method employed within the larger framework of system approach.
- System Analysis: System analysis utilizes the principles and concepts derived from system approaches as the cornerstones for its methodology, to achieve an in-depth examination of any given system under investigation.
System analysis uses tools and techniques to examine and improve specific systems, while system approach provides the overall framework for understanding and overseeing them. The system approach provides a conceptual framework for comprehending systems as an entity; system analysis is one method within the broader system approach used to examine and improve specific systems.
.While system approach focuses on holistic perspectives, interdependencies, and contextual considerations within systems; system analysis offers systematic approaches for examining and improving specific ones within this broader framework.
Conclusion
System Approach and System Analysis are invaluable tools in understanding complex systems and solving problems effectively. By taking a holistic view, businesses, organizations, and individuals can optimize their processes and decision-making, leading to improved efficiency and success.